Sales Incentive Programs A Comprehensive Guide
Sales incentive programs are crucial for driving sales performance and motivating teams. They go beyond simple compensation, offering a structured approach to rewarding and recognizing top performers. This guide delves into the intricacies of designing, implementing, and managing effective sales incentive programs, considering various program types, performance metrics, and specific sales roles. From understanding the fundamentals to exploring innovative approaches, this resource equips readers with the knowledge to craft impactful and successful sales incentive strategies.
The discussion covers a wide spectrum of topics, including defining different types of incentive programs, like commissions and bonuses, and explaining how to design them to align with overall business objectives. It also explores essential performance metrics, outlining how to effectively measure sales success and tailor incentives to different roles. Finally, the guide offers practical steps for implementing and managing these programs, highlighting the importance of communication and feedback throughout the process.
Defining Sales Incentive Programs
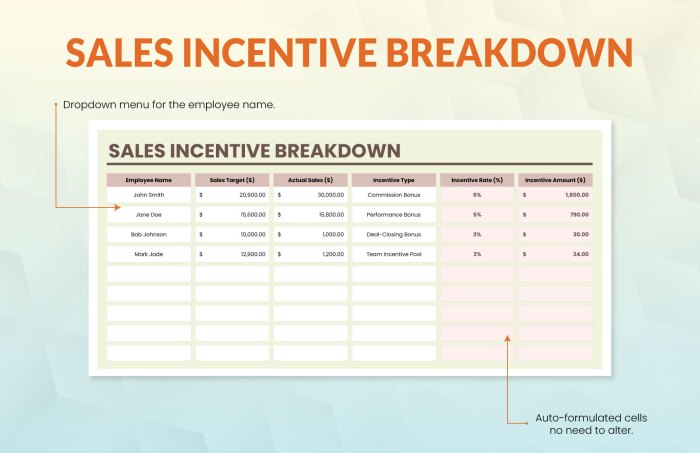
Source: template.net
Sales incentive programs are crucial components of a successful sales strategy. They motivate and reward sales teams for achieving specific targets, driving increased productivity and revenue generation. These programs go beyond standard compensation structures, offering extra motivation to exceed expectations. A well-designed incentive program can significantly impact sales performance, leading to a positive ripple effect throughout the organization.
These programs are designed to create a direct link between performance and reward, fostering a culture of achievement and recognition within the sales force. They differ from other forms of employee compensation in their performance-based nature, focusing on achieving specific sales goals rather than simply being a part of a standard salary structure.
Key Characteristics of Sales Incentive Programs
Sales incentive programs are distinguished by their focus on performance-based rewards. They are not simply additional compensation; they are designed to drive specific behaviors and outcomes. These programs often have clearly defined targets and metrics for measuring success. A key characteristic is the direct correlation between the achievement of sales goals and the rewards offered.
Types of Sales Incentive Programs
Sales incentive programs come in various forms, each with its strengths and weaknesses. These programs aim to motivate sales representatives to achieve specific sales goals and often include elements of competition and recognition. They are designed to provide an extra incentive for employees to strive beyond their normal responsibilities.
Forms of Sales Incentives
Sales incentive programs often utilize a combination of methods to motivate and reward sales teams. They provide different levels of motivation and recognition to incentivize sales representatives to perform at their best. The various forms can include:
- Commissions: A percentage of sales revenue is paid to the salesperson. This is a common and effective method for motivating sales representatives to generate revenue. It directly links their compensation to the revenue they generate, creating a powerful incentive to achieve sales targets. A high commission rate can result in increased sales volume and higher revenue for the organization.
- Bonuses: A one-time payment awarded for achieving specific sales targets or milestones. Bonuses can be awarded for achieving a specific sales target or for exceeding a sales quota. They are often used as a reward for reaching a significant milestone or achieving exceptional performance, acting as a motivator to exceed expectations.
- Contests: Competitions among sales teams or individuals, often with prizes for winners. Contests are effective for fostering a competitive spirit and driving motivation among sales teams. They can generate enthusiasm and create a sense of camaraderie among sales representatives.
- Recognition: Public acknowledgment of achievements, such as awards, public praise, or featured employee spotlights. Recognition programs can enhance employee morale and boost overall team performance. They can take the form of employee of the month programs or other similar forms of recognition.
Comparison of Sales Incentive Program Types
The table below articulates the key characteristics of different types of sales incentive programs:
| Program Type | Description | Example | Pros |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commission | A percentage of sales revenue is paid to the salesperson. | A salesperson earns 10% commission on every sale. | The direct link between performance and reward motivates revenue generation. |
| Bonus | A one-time payment for achieving specific targets or milestones. | A bonus of $500 for exceeding the monthly sales quota. | Motivates achievement of specific goals, provides extra reward for exceptional performance. |
| Contests | Competitions among sales teams or individuals. | A sales contest with prizes for top performers in a quarter. | Fosters a competitive spirit and drives motivation and camaraderie. |
| Recognition | Public acknowledgment of achievements. | Employee of the month award. | Enhances morale, boosts team performance, and provides a sense of accomplishment. |
Designing Effective Incentive Programs
Source: freshworks.com
Crafting a successful sales incentive program requires careful planning and execution. A poorly designed program can demotivate sales teams and fail to achieve desired business objectives. Conversely, a well-structured program can significantly boost performance, driving revenue and achieving strategic goals. Understanding the critical factors and implementing a well-defined strategy are paramount to success.
Effective incentive programs are not just about rewarding sales; they are about aligning individual performance with the overall business objectives. This alignment is achieved by carefully considering the specific goals, metrics, and reward structures. By thoughtfully designing and implementing a program, businesses can foster a more motivated and productive sales force, leading to tangible improvements in key performance indicators.
Crucial Factors to Consider
Designing an effective incentive program requires a thorough understanding of several crucial factors. These include clearly defined goals, relevant performance metrics, a fair and transparent reward structure, and effective communication strategies. Failing to address these factors can lead to a program that is ineffective, demotivating, or even counterproductive.
Aligning Incentives with Business Objectives
Successfully aligning sales incentives with overall business objectives requires a clear understanding of the company’s strategic priorities. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly contribute to achieving these objectives. For example, if a company prioritizes increasing market share, the incentive program should be structured to reward sales representatives who successfully acquire new customers and expand existing relationships.
Steps in Designing a Robust Program
A robust sales incentive program follows a systematic design process. This process involves several key steps, ensuring that the program is aligned with company goals and designed to motivate and reward sales representatives effectively.
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the specific business objectives that the incentive program is designed to support. This should include quantitative targets and measurable outcomes.
- Identify Target Audience: Understand the needs and motivations of the sales team. Different sales teams may respond to different incentives. Tailoring the program to the specific needs of the team is crucial.
- Establish Performance Metrics: Define the specific metrics that will be used to evaluate sales performance. These metrics should be relevant to the company’s objectives and communicated to the sales team.
- Design the Reward Structure: Develop a transparent and equitable reward structure based on the established performance metrics. Consider various reward options, such as commissions, bonuses, and recognition programs.
- Pilot and Refine: Implement a pilot program to test the effectiveness of the incentive structure before a full rollout. Collect feedback from the sales team and adjust the program as needed.
Implementing a New Incentive Program
Implementing a new sales incentive program requires a structured approach. This ensures a smooth transition and maximizes the program’s impact. It’s essential to communicate the program clearly and transparently to the sales team, providing all the necessary information for understanding how it works and how their performance will be evaluated.
- Communication is Key: Communicate the program’s details to the sales team, including the objectives, metrics, reward structure, and any deadlines. Provide ample opportunity for questions and address concerns.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to sales representatives on how to understand and utilize the new program effectively. Offer ongoing support and guidance.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Track the program’s performance against the established metrics and objectives. Regularly assess its effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a mechanism for collecting feedback from the sales team. This allows for ongoing improvement and adjustments to the program based on real-world experience.
Key Elements of an Incentive Program
A well-structured sales incentive program includes several crucial elements. These elements are fundamental to the success of any incentive program.
| Element | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Target Goals | Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives that the program aims to achieve. | Defines the desired outcome and provides a clear direction for the program. |
| Metrics | Quantifiable measures are used to assess sales performance and determine rewards. | Provides a fair and transparent basis for evaluating performance and awarding rewards. |
| Reward Structure | Clear guidelines outlining how rewards are determined based on performance metrics. | Ensures fairness and motivates sales representatives to achieve higher performance. |
| Communication Plan | Strategies for effectively communicating the program’s details to the sales team. | Ensures that the sales team understands the program and how to participate effectively. |
Types of Sales Performance Metrics
Sales performance metrics are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of sales teams and individual representatives. Properly chosen metrics allow businesses to identify areas for improvement, track progress towards targets, and adjust strategies accordingly. A robust system of metrics supports the design of effective incentive programs, ensuring alignment with overall business objectives.
Effective sales incentive programs often hinge on the precise measurement of performance. Understanding the diverse types of metrics, their nuances, and how they relate to different incentive structures is essential for crafting programs that drive optimal results. Different metrics can be weighted differently depending on the specific industry and company culture, but all metrics should align with overarching business goals.
Key Sales Performance Metrics
Understanding the various key metrics used to evaluate sales performance is paramount. These metrics offer valuable insights into team and individual effectiveness, allowing for adjustments and improvements in sales strategies. A thorough grasp of these metrics is essential for the creation of successful incentive programs.
- Revenue Generated: This is a fundamental metric representing the total income generated by sales activities. It’s a direct measure of the team’s ability to close deals and drive revenue. High revenue often indicates strong sales efforts, leading to positive financial outcomes.
- Sales Volume: This metric tracks the total number of units sold. It’s particularly relevant for businesses focused on volume sales, and it provides a different perspective from revenue, highlighting the scale of sales activity. In a competitive market, sales volume can be a critical differentiator.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric measures the cost associated with acquiring a new customer. It’s essential for assessing the efficiency of sales efforts and marketing campaigns. Lower CAC typically signifies more effective sales and marketing strategies.
- Average Deal Size: This metric represents the average value of a sales deal. It provides insights into the sales team’s ability to secure larger contracts and more profitable sales. This metric is valuable in understanding sales strategies that encourage larger deals.
- Conversion Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of leads that are converted into paying customers. A higher conversion rate suggests effective sales processes and a strong sales pipeline.
Quantifiable vs. Qualitative Metrics
Incentive programs benefit from a combination of quantifiable and qualitative metrics. Quantifiable metrics, like revenue or sales volume, provide clear numerical data for evaluation and comparison. Qualitative metrics, such as customer satisfaction or product knowledge, offer a more nuanced understanding of the sales process and the salesperson’s skills.
- Quantifiable Metrics: These metrics are objective and measurable, allowing for precise tracking and comparison. Examples include revenue, sales volume, and conversion rates. They provide a clear picture of sales performance, making it easier to identify areas for improvement and to track progress towards targets.
- Qualitative Metrics: These metrics are subjective and are often assessed through surveys or feedback. Examples include customer satisfaction scores, product knowledge, and sales presentation skills. They offer insights into the sales process, salesperson interactions, and the overall customer experience. Combining quantifiable and qualitative metrics provides a comprehensive understanding of sales performance.
Pros and Cons of Different Metrics
Using different metrics in incentive programs has advantages and disadvantages. The best approach involves carefully considering the specific goals and context of the incentive program.
| Metric | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | Direct measure of success, easily trackable, aligned with company goals. | Doesn’t account for sales volume and can incentivize short-term gains over long-term customer relationships. |
| Sales Volume | Tracks overall activity and can identify sales trends. | Doesn’t account for profitability and may incentivize quantity over quality. |
| Customer Acquisition Cost | Evaluates sales and marketing effectiveness, drives efficiency. | Difficult to isolate sales contribution, which requires robust data tracking. |
| Average Deal Size | Encourages larger deals and improves profitability. | Can be affected by external factors, may not reflect individual sales efforts. |
| Conversion Rate | Highlights sales process effectiveness and identifies bottlenecks. | Can be influenced by factors outside sales control, may not reflect overall revenue impact. |
Examples of Metrics in Different Scenarios
Different sales scenarios require different metrics. Tailoring metrics to the specific context is essential for designing effective incentive programs.
- New Product Launch: Metrics like sales volume and conversion rate are crucial to gauge initial product reception. Tracking the number of leads generated and the time to close deals can help optimize the sales process.
- Existing Product Sales: Revenue and average deal size might be more important. Incentivizing upselling or cross-selling opportunities can increase profitability.
- High-Value Accounts: Customer acquisition cost and lifetime value (CLTV) become critical metrics. Building strong relationships and retaining high-value clients are paramount.
Implementing and Managing Sales Incentives: Sales Incentive Programs
Successfully implementing and managing a sales incentive program is crucial for driving sales performance and maintaining a motivated sales team. A well-structured program, carefully managed, can significantly boost revenue and employee engagement. Conversely, a poorly implemented program can lead to frustration, inequity, and decreased overall effectiveness.
Effective Implementation Procedures
Implementing a sales incentive program requires a systematic approach. This involves clearly defining program goals and aligning them with overall business objectives. Thorough communication is paramount, ensuring all sales representatives understand the program’s rules, eligibility criteria, and reward structure. A well-defined timeline, with specific deadlines for program milestones, is essential to maintain momentum and avoid delays. Documenting all aspects of the program, including program rules, eligibility, and communication, is critical for future reference and potential audits.
Monitoring and Evaluation Strategies
Monitoring program effectiveness is essential to ensure it meets its objectives. This involves tracking key metrics, such as sales volume, conversion rates, and customer acquisition costs. Regular reports and analyses should be generated to assess program performance against established benchmarks. This data allows for adjustments and refinements to optimize the program’s impact. Utilizing data visualization tools can effectively present key performance indicators (KPIs) and facilitate a deeper understanding of program effectiveness.
Communication and Feedback Mechanisms
Open communication channels are vital for a successful incentive program. Sales representatives should receive regular updates on program progress and performance. Feedback mechanisms, such as surveys and one-on-one meetings, allow for identifying areas for improvement and addressing concerns promptly. This two-way communication fosters a sense of transparency and trust, which are crucial for employee engagement and motivation.
Handling Potential Challenges and Obstacles
Anticipating and addressing potential challenges is crucial for a smooth program launch. One common challenge is ensuring fairness and equity across the sales team. Clear criteria and transparent processes help prevent disputes and maintain morale. Another potential obstacle is fluctuating market conditions. Adaptability is key; the program should be flexible enough to accommodate changing market demands and sales patterns. Building a robust support system for handling program-related inquiries and issues is also essential.
Checklist for Launching a New Sales Incentive Program
- Define clear program goals and objectives, aligning them with overall business strategies. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Establish eligibility criteria, ensuring fair and transparent participation guidelines.
- Develop a comprehensive reward structure, detailing the various levels of incentives and associated performance targets. Examples of reward structures include tiered commissions, bonuses, or gift cards.
- Create detailed program documentation, including guidelines, eligibility requirements, and communication protocols.
- Design a robust communication plan, outlining how the program will be communicated to the sales team. This plan should include the frequency of updates and methods of communication.
- Establish a monitoring system, tracking key metrics and generating regular reports on program performance. Data should be analyzed to identify areas of improvement.
- Develop a feedback mechanism, allowing for input and addressing concerns promptly.
- Implement a system for handling potential disputes and issues related to the program. Having a defined escalation process is essential.
- Create a detailed timeline with specific deadlines for program milestones. This will ensure a smooth and timely implementation.
Impact and Effectiveness of Sales Incentives
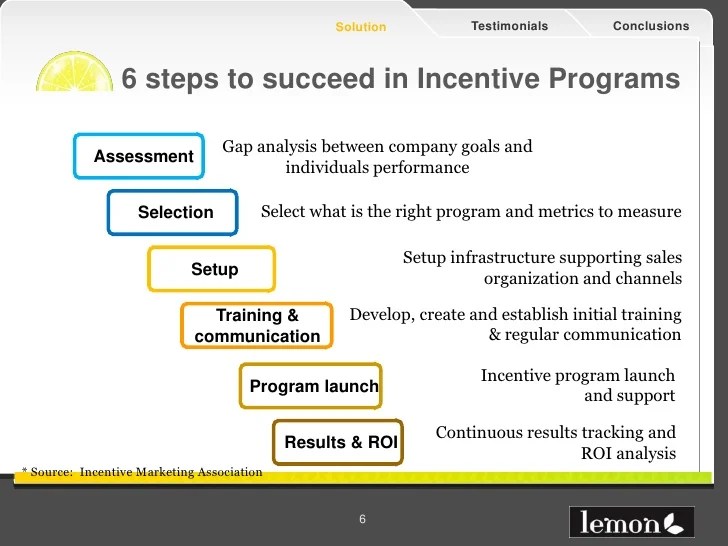
Source: slidesharecdn.com
Sales incentive programs are a powerful tool for driving sales performance, but their success hinges on careful planning and execution. Understanding the factors influencing their effectiveness is crucial for maximizing returns on investment. A well-designed program can boost morale, motivate teams, and significantly impact overall revenue. Conversely, poorly implemented programs can lead to decreased productivity and wasted resources.
A successful sales incentive program isn’t just about offering rewards; it’s about aligning the rewards with the company’s strategic goals and effectively communicating the program’s purpose to the sales team. This requires a deep understanding of the target market, sales processes, and individual team dynamics.
Factors Influencing Incentive Program Success
Several key factors play a crucial role in determining the success of a sales incentive program. These include clear program objectives, well-defined target audiences, and a well-structured reward system. Alignment with overall business strategy is essential to ensure that incentives drive desired behaviors and outcomes. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the sales team’s needs and motivations is vital for program effectiveness.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Incentive Programs
Numerous examples illustrate the impact of well-structured and poorly structured sales incentive programs. A successful program at a software company, for example, tied rewards to customer acquisition and retention, leading to a 20% increase in sales within six months. Conversely, a program focused solely on individual quotas without considering team collaboration at a retail outlet resulted in increased competition and decreased overall sales. This highlights the importance of considering teamwork and collaboration alongside individual targets.
Evaluating the Impact of a Sales Incentive Program
Evaluating the impact of a sales incentive program requires a structured approach. This involves meticulously tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) before, during, and after the program’s implementation. This data provides valuable insights into the program’s effectiveness and allows for adjustments and improvements. Analyzing the program’s results about pre-set goals and objectives is essential for determining its impact.
Key Indicators of Program Success
The success of a sales incentive program is not solely measured by increased sales figures. Various key indicators provide a comprehensive view of the program’s impact. These include improved sales conversion rates, increased customer satisfaction, enhanced team morale, and a reduction in sales cycle times. Qualitative feedback from the sales team and customers is also valuable.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of a Successful Incentive Program
The following table shows ArtArtikel’sy performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of a sales incentive program. These metrics provide a structured framework for evaluating the program’s effectiveness.
| KPI | Description | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Growth | Percentage increase in sales revenue compared to the previous period. | 15-20% |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Cost incurred to acquire a new customer. | Reduced by 10% |
| Average Sales Cycle Time | Average time taken to close a sale. | Reduced by 5 days |
| Sales Team Morale | Measured through surveys and feedback. | Increased by 15% |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of customers retained over a specific period. | Increased by 5% |
Incentive Programs for Specific Sales Roles

Tailoring sales incentive programs to the unique characteristics of different sales roles is crucial for maximizing performance and engagement. Understanding the distinct challenges and opportunities within each role allows for the design of programs that effectively motivate and reward specific behaviors. This approach fosters a more targeted and impactful incentive structure.
Incentive programs should not be one-size-fits-all. Inside sales representatives, outside sales teams, and account managers all have different needs and priorities. Effective programs acknowledge these differences and create structures that align with the unique demands and requirements of each role.
Inside Sales Incentive Program Design
Inside sales teams often excel at high-volume transactions and consistent follow-up. Incentive programs for this role should focus on quantifiable metrics like the number of qualified leads generated, appointments scheduled, and sales closed. A commission structure tied to these metrics is highly effective. Rewarding consistent performance and quick response times is key.
Outside Sales Incentive Program Design
Outside sales teams face different challenges, including building relationships and closing complex deals. Incentives should emphasize deal size, customer acquisition, and account expansion. Programs that include a combination of commission structures and performance-based bonuses based on achieving specific quotas and targets are often successful.
Account Management Incentive Program Design
Account management focuses on building and maintaining long-term relationships with key clients. Incentive programs for this role should emphasize client retention, upselling, and cross-selling activities. Incentivizing the development of strong customer relationships and the pursuit of higher revenue streams from existing accounts is important.
Comparison of Incentive Program Structures Across Sales Roles
The table below highlights the key differences in incentive program design across various sales roles.
| Sales Role | Program Focus | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Inside Sales | High volume, consistent follow-up, lead generation | Number of qualified leads, appointments scheduled, sales closed, conversion rates |
| Outside Sales | Relationship building, complex deal closing, customer acquisition | Deal size, customer acquisition, account expansion, contract value |
| Account Management | Client retention, upselling, cross-selling, relationship development | Client retention rate, upsell revenue, cross-sell revenue, customer satisfaction scores |
Tailoring Incentives to Specific Sales Team Needs
Understanding the specific needs and motivations of different sales teams is paramount. For instance, a team focused on high-volume sales might be highly motivated by a commission structure based on individual performance, while a team focusing on long-term client relationships might prefer incentives that recognize consistent effort and client satisfaction. Consider team dynamics, individual personalities, and market conditions when designing the program.
Examples of Innovative Sales Incentive Programs
Innovative sales incentive programs go beyond basic commissions and bonuses, often incorporating unique elements to boost motivation, foster creativity, and drive exceptional results. These programs frequently address specific challenges within a sales team or industry, leading to improved performance and increased profitability. A well-designed program can be a powerful tool to drive positive change and improve overall sales performance.
These programs aren’t just about rewarding top performers; they are designed to inspire and motivate the entire sales force. They recognize that a strong sales team is built on a foundation of shared goals, collaborative efforts, and a culture of continuous improvement. This often results in increased sales volume, higher customer satisfaction, and a more engaged and productive sales team.
Examples from Different Industries
Sales incentive programs can be tailored to fit the specific needs and characteristics of various industries. By understanding the unique dynamics of each industry, program designers can create incentives that effectively motivate and reward employees while aligning with company goals.
- Technology Industry: A software company might implement a “customer success” incentive program that rewards sales representatives for exceeding customer satisfaction metrics, such as the average customer support ticket response time. This approach emphasizes long-term customer relationships and value creation over just the initial sale. The program addresses the challenge of maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty in a competitive market.
- Retail Industry: A large retail chain could offer a tiered incentive program based on sales volume, product variety sold, and customer retention. Each tier unlocks additional rewards and recognition, creating a sense of progression and accomplishment. This approach helps address the challenges of motivating sales staff in a competitive retail environment. Incentivizing product diversity beyond the most popular products is key to increasing sales volume across the product portfolio.
- Financial Services Industry: A financial advisory firm could establish a “knowledge sharing” incentive program where sales representatives earn points for participating in internal training sessions, mentoring colleagues, or developing new financial products. This fosters a culture of learning and collaboration. The program addresses the need for continuous professional development and a more supportive work environment, which is critical for financial advisors who need to continuously improve their skills and knowledge. It also increases the internal knowledge base and creates opportunities for employees to learn and share with their peers.
Innovative Incentive Programs
Companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of designing programs that cater to the specific motivations and needs of their sales teams. Innovative programs often incorporate a variety of elements, such as gamification, recognition programs, and peer-to-peer contests.
A software company implemented a “Sales Champions” program. Instead of focusing solely on individual sales volume, the program recognized teams who successfully closed deals in collaboration. Sales representatives earned points for contributing to a deal, not just for closing it. This innovative approach addressed the challenge of fostering teamwork and collaboration within a sales team focused on individual performance. The program awarded prizes to the top-performing teams and highlighted their success to boost morale and motivation across the entire sales force.
Final Review
In conclusion, crafting successful sales incentive programs requires a deep understanding of various factors, from program design and implementation to performance measurement and management. By considering the unique characteristics of different sales roles, tailoring incentives to specific needs, and focusing on clear communication and feedback, companies can create programs that drive exceptional results. This guide provides a comprehensive framework for building and managing incentive programs that motivate top performance and ultimately contribute to overall business success.





